With over 20 years of experience in the recycling and scrap industry, I’ve been at the forefront of one of the most critical challenges of the 21st century: electronic waste. As technology rapidly advances, so does the rate at which devices become obsolete. This results in a growing pile of discarded electronics – commonly known as “e-waste.” But what is e-waste recycling, and why is it paramount? Dive into this guide as I share my insights and expertise.
Key Takeaways:
- E-waste recycling is an environmentally responsible approach to managing discarded electronic devices.
- The objective is to divert e-waste from landfills, preventing harmful chemical releases.
- Recycling e-waste recovers valuable materials like metals, plastics, and glass.
- This process reduces the need for virgin resources, lowering electronics manufacturing’s environmental footprint.
- Proper e-waste management protects our environment and conserves essential resources.

Demystifying E-Waste
Before diving into the recycling process, understanding what e-waste entails is crucial.
E-Waste Defined
E-waste, or electronic waste, encompasses discarded electronic devices and components. Examples include old computers, smartphones, tablets, televisions, and printers.
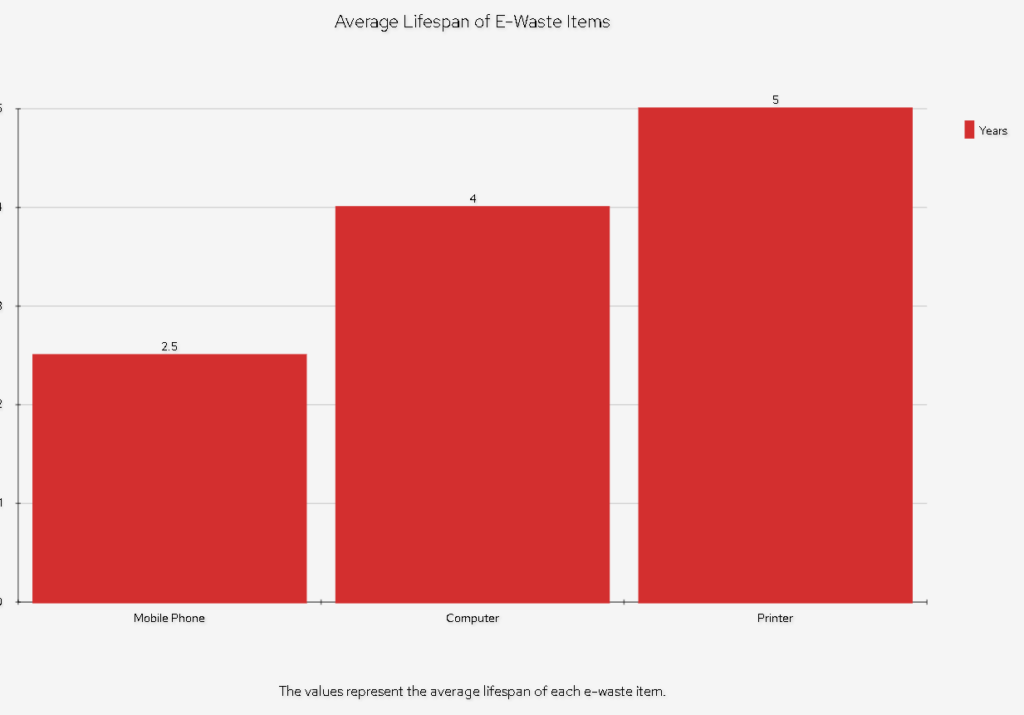
Table: Common E-Waste Items and Their Lifespans
| Device | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Computers | 3-5 years |
| Smartphones | 2-3 years |
| Televisions | 5-10 years |
Why E-Waste Recycling Matters
Electronic waste is more than just an environmental concern; it’s a significant health and economic issue.
The rapid technological advancements lead to a shorter lifespan of electronic devices. When not disposed of properly, they can lead to e-waste pollution, contaminating soil and water with harmful chemicals.
E-Waste’s Environmental and Health Hazards
Electronic devices house harmful substances like lead, mercury, and specific flame retardants. These toxins can seep into soil and water sources, posing grave environmental and health risks.
Conservation of Valuable Resources
E-waste is rich in valuable resources such as gold, silver, and copper. Recycling ensures these materials are reclaimed, reducing the demand for new raw materials.
The E-Waste Recycling Process
E-waste recycling isn’t merely about dumping electronic junk into bins. It’s a meticulous process ensuring both environmental and resource conservation.
Collection
Everything starts with gathering the e-waste. This involves designated recycling programs, drop-off locations, or specialized collection events.
Sorting and Disassembly
Post-collection, e-waste is sorted into categories. Components are then separated from the devices to isolate reusable materials.
Hazardous Material Removal
Safeguarding our environment requires carefully removing and disposing of hazardous substances contained within e-waste.
Material Recovery
Advanced mechanical and chemical processes reclaim valuable materials from the e-waste.
Recycling and Reuse
The retrieved materials undergo processing, readying them for reintroduction into new electronic products or other manufacturing processes.
Proper Disposal
Any residual non-recyclable or hazardous waste gets disposed of in alignment with stringent environmental regulations.
Examples of E-Waste Items
To better understand the scope of the issue, here are some e-waste examples:
- Mobile phones
- Televisions
- Refrigerators
- Microwaves
- Digital cameras

Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is e-waste or electronic waste? E-waste, short for electronic waste, refers to discarded electronic or electrical devices.
- What is e-waste mining? E-waste mining refers to extracting valuable metals and materials from e-waste.
- Why is e-waste considered a problem? Besides environmental concerns, improper e-waste disposal can lead to health issues due to toxins and can result in the waste of valuable resources.
- Are all electronic devices recyclable? While most components of electronic devices can be recycled, certain parts might need specialized disposal methods due to their hazardous nature.
- Why is e-waste recycling important? Recycling e-waste helps reduce environmental pollution and conserve natural resources by reclaiming valuable materials from discarded electronics.
- How can individuals contribute to e-waste management? Ensuring proper disposal of electronic items either by recycling or donating them to certified facilities or organizations.
In conclusion, e-waste recycling is more than just an environmental initiative. It’s a comprehensive approach to responsibly managing our electronic consumption. As we continue to embrace technology, understanding and implementing responsible e-waste recycling practices become imperative for a sustainable future.
